He discriminatory power of CGH is larger than that of MLST
페이지 정보
작성자 Alfonzo 댓글 0건 조회 5회 작성일 23-09-29 07:35본문
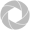
He discriminatory power of CGH is larger than that of MLST analysis, since isolates that belong to MLST CC1 can be divided into subclusters using CGH. Moreover,Vietnamese isolates that belong to different pulse field types, were assigned to the same CGH subcluster [6]. This could be explained by genomic inversions and substitutions, that were observed in the genome of the Vietnamese reference strain BM407 in comparison to P1/de Greeff et al. BMC Microbiology 2011, 11:161 http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2180/11/Page 12 ofFigure 4 Representation of COG categories among the core genome. Relative representation of COG categories in the whole genome (hatched bars) compared to the core genome (black bars) of S. suis strain P1/7. Representation is calculated as the percentage of genes per COG category compared to the total number of genes in the genome. COG categories: J translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis; K transcription; L replication, recombination and repair; D cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning; V defense mechanisms; O posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones; M cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis; N cell motility; U intracellular trafficking, secretion, and vesicular transport; T signal transduction mechanisms; C energy production and conversion; P inorganic ion transport and metabolism; G carbohydrate transport and metabolism; E amino acid transport and metabolism; F nucleotide transport and metabolism; H coenzyme transport and metabolism; I lipid transport and metabolism; Q secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism; R general function prediction only; S function unknown; `other' no COG category attached.[7]. These changes can be discriminated by PFGE, but not by CGH. To correlate PubMed ID:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10956013 virulence of isolates to CGH results, virulence of serotype Capecitabine 1 and serotype 9 isolates was determined in an experimental infection. For serotype 1, our animal experiment showed that in contrast to the field isolates, the reference strain was not highly virulent. Since serotype 9 only induced clinical symptoms at very high doses, we concluded that serotype 9 isolates were avirulent under experimental conditions. This was confirmed by other studies [32,33]. To correlate virulence to CGH data, distribution of 25 putative virulence genes among S. suis isolates was studied. Each CGH cluster was shown to be associated with a specific profile of putative virulence genes. Cluster A isolates contained all 25 putative virulence genes. Cluster B isolates on the contrary lacked up to 12 putative virulence genes among which one or more of sortase genes (srtBCD, srtE, srtF) that are involved in assembly of pili [31,34].In agreement with data presented here, Takamatsu et al. showed that CC1 isolates contained all srt genes, whereas CC29 isolates lacked srtBCD genes [34]. However, none of our serotype 9 isolates contained the srtBCD gene cluster, whereas this cluster was detected in a Japanese serotype 9 isolate [34]. This could imply geographical variation. Moreover, the revs gene is absent from all cluster B isolates, with the exception of cluster B5 isolates. This regulator influences expression of putative virulence factors [35]. Therefore, lack of revs might affect virulence of isolates. The IgA1 protease gene was found to be absent in all serotype 9 isolates, and displayed extensive sequence variation in serotype 7 isolates. All serotype 2 isolates including the avirulent isolates contained.
댓글목록
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.